Table of Contents
Understanding 97110 vs 97530 is essential for accurate documentation, clean billing, and preventing costly denials. These two CPT codes Therapeutic Exercise (97110) and Therapeutic Activity (97530) are frequently misunderstood because they share similar goals yet represent very different types of interventions.
This guide explains when to use each code, key documentation requirements, billing rules, examples, and how an EMR like HelloNote helps streamline compliant coding.
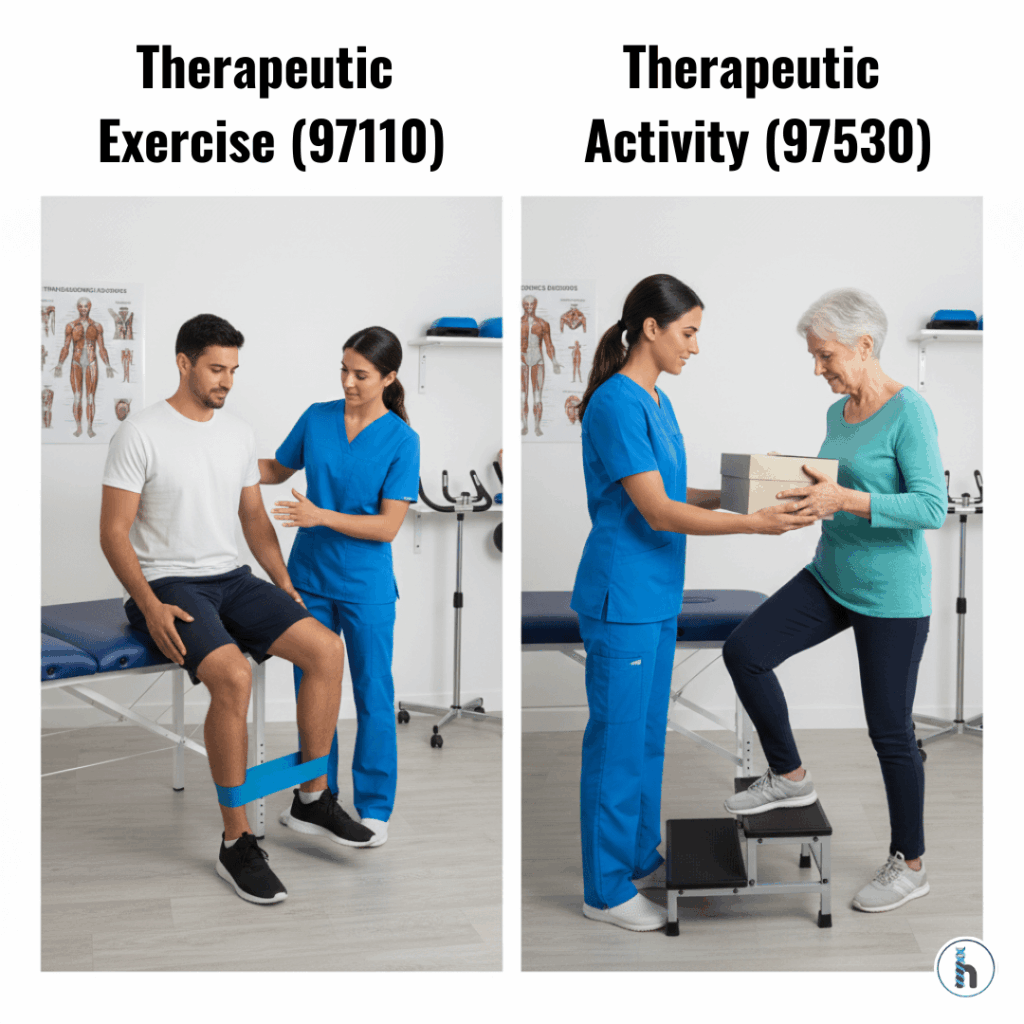
What’s the Difference Between 97110 and 97530?
Therapeutic exercise and therapeutic activity are both time-based CPT codes used by PT, OT, and SLP professionals. However, they address different clinical purposes.
Why Choosing the Right CPT Code Matters
Selecting the incorrect code can result in:
Reduced reimbursement
Compliance risks
Increased audit exposure
Understanding 97110 vs 97530 ensures you bill accurately and reflect true clinical intent.
CPT Code 97110 Therapeutic Exercise
What Is 97110?
Structured exercises used to improve strength, flexibility, ROM, or endurance.
Required Documentation for 97110
Documentation must include:
Body region treated
Specific muscles or joints
Purpose of each exercise
Relation to functional goals
Examples of 97110 Exercises
ROM exercises
Resistance training
Aerobic conditioning
Stretching
CPT Code 97530 Therapeutic Activities
What Is 97530?
Functional, dynamic, real-world activities that simulate daily tasks.
Required Documentation for 97530
Documentation should show:
Real-life task simulation
Functional significance
Multiple movement components
Direct link to functional goals
Examples of 97530 Activities
Lifting and carrying objects
Stair training
Reaching while balancing
Simulated transfers
Billing Guidelines for 97110 vs 97530
Both codes follow:
15-minute increments
Using Modifier 59
Required when billing both codes in the same session.
Insurance Considerations
Medicaid: Often covers 97530, not always 97110
Private payers: Usually reimburse both with clear documentation
Medicare: Rates vary; 97530 often reimburses slightly higher
Common Reasons for Claim Denials
Insufficient Documentation
Vague vs. detailed examples included.
Incorrect Dual Billing
Must justify why both codes were used.
Time Rule Errors
Failure to meet the 8-minute rule leads to denials.
How HelloNote EMR Simplifies 97110 vs 97530 Coding
HelloNote helps clinics by:
Auto-applying modifiers
Providing documentation guidance
Validating codes before claim submission
Tracking progress and medical necessity
Final Thoughts on 97110 vs 97530
Mastering these distinctions helps ensure:
Accurate documentation
Fewer denials
Higher reimbursement
Better compliance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
97110 focuses on improving measurable physical components like strength, endurance, or range of motion. In contrast, 97530 targets functional, real-world activities such as lifting, reaching, transfers, or stair climbing. If the activity simulates daily tasks and involves multiple movement parameters, it should be billed under 97530.
Yes — but only if each service is distinct and separately documented. Modifier 59 must be applied to indicate that the therapist provided two unique interventions with different goals. Without clear documentation, payers may deny one of the codes as duplicate billing.
CPT 97530 (Therapeutic Activity) generally reimburses at a higher rate because it involves more complex, functional, and task-oriented interventions. However, exact reimbursement varies by payer, state, and contract.
Coverage varies by state. Many Medicaid programs reimburse 97530 but have stricter limitations or exclusions for 97110. Clinics must verify Medicaid coverage for each patient before billing to prevent denials.
HelloNote automates modifier logic, validates CPT code selection, and prompts therapists when documentation is incomplete. It streamlines billing, reduces denials, and ensures compliance with 97110 vs 97530 rules, helping clinics protect revenue and improve claim approval rates.