Table of Contents
The 8-minute rule is one of the most important Medicare billing guidelines for therapy providers. If you work in outpatient rehab PT, OT, or SLP this rule determines how many billable units you can charge based on timed interventions. Understanding the 8-minute rule prevents underbilling, reduces denials, and keeps your clinic compliant.
This guide breaks down the rule in simple terms and shows how HelloNote EMR helps therapists stay accurate without extra math or guesswork.
What Is the 8-Minute Rule?
According to CMS:
“For any single timed CPT code measured in 15-minute units, providers may bill one unit when treatment is 8 minutes or more, up to 22 minutes.”
Why it matters:
Even though units are 15 minutes long, therapists may bill starting at 8 minutes which is why it’s called the 8-minute rule.
The 8-minute rule applies only to Medicare and some commercial payers that follow CMS guidelines.
Time-Based vs. Service-Based CPT Codes
Correct billing depends on knowing which CPT codes follow the 8-minute rule.
Time-Based Codes (Subject to the 8-Minute Rule)
These require documenting how long the patient received skilled therapy:
Therapeutic exercise
Therapeutic activity
Neuromuscular re-education
Manual therapy
Gait training
Self-care training
These codes must follow the 8-minute rule for units.
Service-Based Codes (Not Time-Dependent)
These codes are billed once per session, regardless of total time:
PT/OT/SLP evaluations
Re-evaluations
Hot/cold packs
Mechanical traction
These do not follow the 8-minute rule.
How the 8-Minute Rule Works (With Clear Examples)
Billing becomes much easier when you focus on total timed treatment minutes and how the 8-minute rule assigns units.
Example 1 — Two Timed Codes
15 minutes → Therapeutic Activity
10 minutes → Therapeutic Exercise
Total timed minutes: 25
Billing under the 8-minute rule:
1 unit TA
1 unit TE
Example 2 — Mixing Timed & Untimed Codes
10 minutes → Therapeutic Activity
10 minutes → Manual Therapy
10 minutes → Cold Pack (service-based)
Cold pack = 1 unit (not timed)
Total timed minutes = 20
Under the 8-minute rule, 20 minutes = 1 billable unit
You may choose the higher-value code.
Example 3 — Using the Remainder Rule
12 minutes → Therapeutic Activity
22 minutes → Neuromuscular Re-Education
7 minutes → Therapeutic Exercise
Total timed minutes = 41
The 8-minute rule allows 3 units:
2 units Neuromuscular Re-Ed
1 unit Therapeutic Activity
Even though TE was only 7 minutes, it contributes to total timed minutes.
Common Challenges When Applying the 8 Minute Rule
Confusion About Remainder Rule
The biggest error clinics make is miscalculating the final leftover minutes, which determines whether a unit is lost or gained.
Underbilling
Forgetting to combine all timed minutes often results in lost revenue.
Mislabeling Timed vs. Untimed Codes
This leads to denials and payer audits.
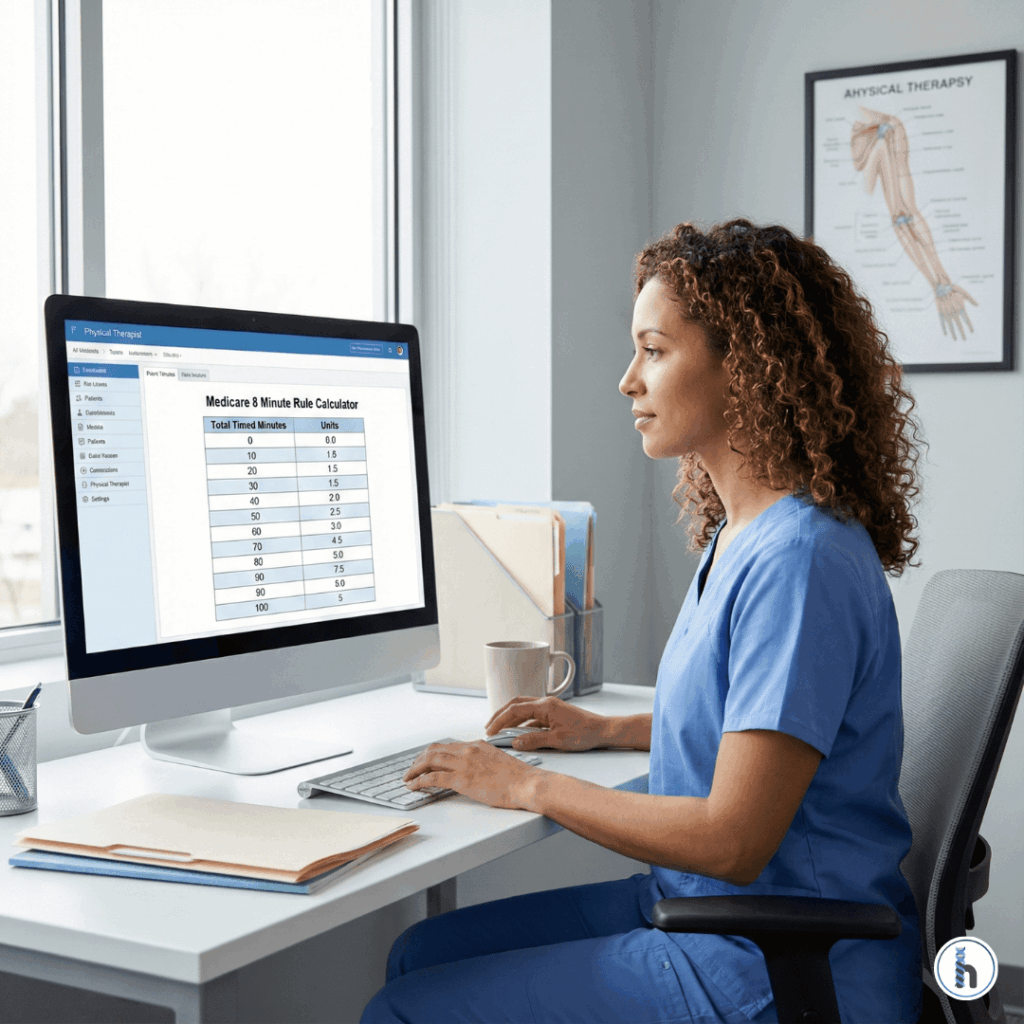
How HelloNote EMR Simplifies the 8 Minute Rule
Billing based on the 8-minute rule can get complex especially when juggling multiple codes. HelloNote eliminates the confusion with:
Built-in 8-minute rule calculators
Automatic unit recommendations
Alerts for inconsistent documentation
Correct CPT assignment for each visit
Clean claim formatting to reduce denials
With HelloNote, therapists avoid miscalculations and focus on patient care not math.
Key Takeaways for Therapists
Always calculate total timed minutes
Apply the 8 minute rule to determine billable units
Use the remainder rule for accuracy
Service-based codes are never timed
EMR support prevents billing errors
Mastering the 8-minute rule ensures clean claims, faster payments, and fewer billing headaches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The 8-minute rule allows therapists to bill one unit when at least 8 minutes of a timed CPT code are performed.
Medicare and insurance companies that adopt CMS guidelines require compliance with the 8-minute rule.
No. Service-based codes (modalities, evals) are billed once per session regardless of time.
Add all timed minutes → use the CMS chart → assign units based on remainder minutes.
HelloNote automates calculations, reduces errors, and ensures your billing aligns with the 8-minute rule every time.