Navigating the complexities of healthcare billing is a fundamental aspect of running a successful rehabilitation therapy practice. Whether you are an Occupational Therapist, Physical Therapist, Speech-Language Pathologist, clinic owner, or administrator, understanding the nuances of claim submission is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow and ensuring compliance. For practices serving Medicare beneficiaries, among the most critical components are the 837P electronic claim format and the traditional Form CMS-1500 paper claim. Demystifying these standards is the first step towards streamlining your Medicare billing for therapy professionals and securing timely reimbursement. This article provides an essential guide to understanding the CMS-1500 form and 837P claims, outlining their roles, requirements for use, key components for accuracy, and how modern tools can simplify this vital operational function. It will help you understand how to bill Medicare for physical therapy and other therapy disciplines effectively.
The Foundation: Understanding 837P and Form CMS-1500
At its core, Medicare billing for professional services hinges on two primary formats:
837P (Professional)
This is the standard electronic format mandated by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for transmitting healthcare claims. Health care professionals, including therapists and suppliers, use the 837P format to submit **837P claims** electronically to Medicare Fee-For-Service (FFS) Contractors (like **Medicare Administrative Contractors or MACs**) and potentially other government and private insurers. It adheres to the specific technical standards set by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) X12N – currently Version 5010A1. Think of the 837P as the digital language computers use to exchange detailed claim information securely and efficiently.
Form CMS-1500
This is the standard paper claim form. While electronic submission is the default and strongly preferred method, the **CMS-1500 form** is permitted under specific circumstances for billing Medicare FFS Contractors. It serves as the hard-copy equivalent of the 837P, containing similar data elements necessary for claim processing. The specific version designation (e.g., 08/05 mentioned in older guidance, updated over time) ensures consistency in processing. Understanding the nuances of **837P vs CMS-1500 for Medicare** is vital for correct submission.
The crucial takeaway is that electronic submission via the 837P format is the standard expectation. The data elements required in the electronic format are designed to be consistent with those on the paper form, allowing processing systems to handle both, but the trend and regulations heavily favor electronic transactions.
The Mandate for Electronic Billing: ASCA Requirements<
The Administrative Simplification Compliance Act (ASCA) generally requires that all initial claims for payment under Medicare be submitted electronically. This push towards electronic claims aims to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and speed up payment processing. For most therapy practices, this means utilizing the 837P format for submitting Medicare claims is not just recommended; it is required for efficient rehabilitation therapy billing.
Exceptions to the Rule: When is Paper (CMS-1500) Permitted?
While electronic submission is the standard, ASCA does allow for certain exceptions and waivers, permitting the use of the paper CMS-1500 form. Therapy practices should carefully assess if they qualify before submitting paper claims:
Small Provider Exception
Practices with fewer than 10 Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) employees are generally considered small and may qualify for this **Medicare billing exception for small practices**, allowing them to submit paper claims without needing a formal waiver request.
Waiver Scenarios
In specific situations, providers can request a waiver from their Medicare FFS Contractor to submit paper claims. Examples might include disruptions in electricity or communication services that are reasonably expected to last longer than two business days, or situations where the staff’s disability prevents the use of a computer for electronic submission. These waivers typically require pre-approval from Medicare.
It is vital for clinic administrators and owners to understand these exceptions. Self-assessing for the small provider exception or proactively applying for a waiver, if applicable, is necessary to ensure compliance when submitting paper claims. However, relying on these exceptions should be carefully considered against the potential delays and inefficiencies compared to electronic submission.
Key Components for Accurate Claim Submission
Whether submitting electronically via 837P or on paper via CMS-1500 form, accuracy is paramount. Errors or omissions can lead to claim rejections, denials, and payment delays, impacting your overall therapy billing compliance. Focus on these critical areas:
Correct Coding: This is non-negotiable.
Diagnosis Codes (ICD-10-CM)
Use the current International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (**ICD-10-CM therapy**) codes. Always code to the highest level of specificity available to accurately reflect the patient’s condition being treated. Ensure the diagnosis justifies the medical necessity of the therapy services provided.
Procedure Codes (HCPCS)
Utilize the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (**HCPCS codes therapy**). This includes Level I codes (Current Procedural Terminology – CPT codes, maintained by the AMA, describing therapy evaluation and treatment services) and Level II codes (alpha-numeric codes identifying products, supplies, and services not included in CPT, like some durable medical equipment or orthotics). Using the correct, current codes for the services rendered is essential for any **Physical Therapist billing** or other therapy professional.
Proper Use of Modifiers
Modifiers provide additional information about a service or procedure without changing the core meaning of the code. They are crucial for accurate billing in therapy. Examples include:
* Modifiers indicating a distinct procedural service (e.g., Modifier 59).
* Modifiers related to specific payment policies or programs (like therapy functional limitation reporting G-codes and severity modifiers in the past, or current quality program requirements).
* Modifiers required for specific circumstances, such as those related to Advance Beneficiary Notices (ABNs) when a service might not be considered medically necessary.
* Therapy discipline modifiers (GP, GO, GN) identifying services furnished under Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy, or Speech-Language Pathology plans of care.
Understanding when and how to apply modifiers correctly is vital for claim acceptance and proper payment.
Documentation Supporting Medical Necessity
Every claim submitted implies that the service provided meets Medicare’s requirements: it falls within a covered benefit category, is not specifically excluded, and is reasonable and necessary for the patient’s condition. Your clinical documentation must clearly support this medical necessity. This documentation is the backbone justifying the codes and modifiers used on your claim.
Accuracy of Information
Ensure all patient demographic information, provider identifiers (like NPI), dates of service, charges, and insurance details are precisely entered. Small errors can cause significant processing delays.
Navigating the Submission Process
Beyond claim content, understanding the logistical aspects of submission is key for effective Medicare billing for therapy professionals:
Timely Filing
Medicare has a strict timely filing limit. Claims must be received by the appropriate Medicare contractor within 12 months (one calendar year) from the date of service. Claims submitted after this deadline will be denied, and this denial is generally not appealable. For services spanning multiple dates, the ‘From’ date on the claim line item is typically used to determine timeliness.
Where to Submit
Submit claims to the correct entity. For traditional Medicare beneficiaries (Medicare FFS), claims go to your designated **Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC)**. However, if the beneficiary is enrolled in a Medicare Advantage (MA) Plan (Part C), claims must be submitted directly to that private MA plan, not the FFS contractor. Verifying patient eligibility and plan type before submitting claims is crucial.
Medicare Secondary Payer (MSP)
Determine if Medicare is the primary or secondary payer. MSP provisions apply when a beneficiary has other insurance coverage (e.g., employer group health plan, workers’ compensation). Correctly identifying the primary payer and coordinating benefits is essential to avoid improper payments and potential recoupments.
Compliance: Protecting Your Practice
Submitting accurate claims is not just about getting paid; it is about maintaining therapy billing compliance and protecting the integrity of the Medicare program. Practices must actively avoid:
Fraud
Knowingly submitting false statements or misrepresenting facts to obtain payment (e.g., billing for services not rendered, falsifying documentation).
Abuse
Practices that result in unnecessary costs to Medicare, often through bending the rules (e.g., improper coding leading to higher payments, providing services that are not medically necessary).
Staying current with Medicare billing policies, ensuring robust documentation practices, and fostering a culture of compliance are critical safeguards for any therapy practice.
Streamlining Billing with Technology: The Role of EMR Systems<
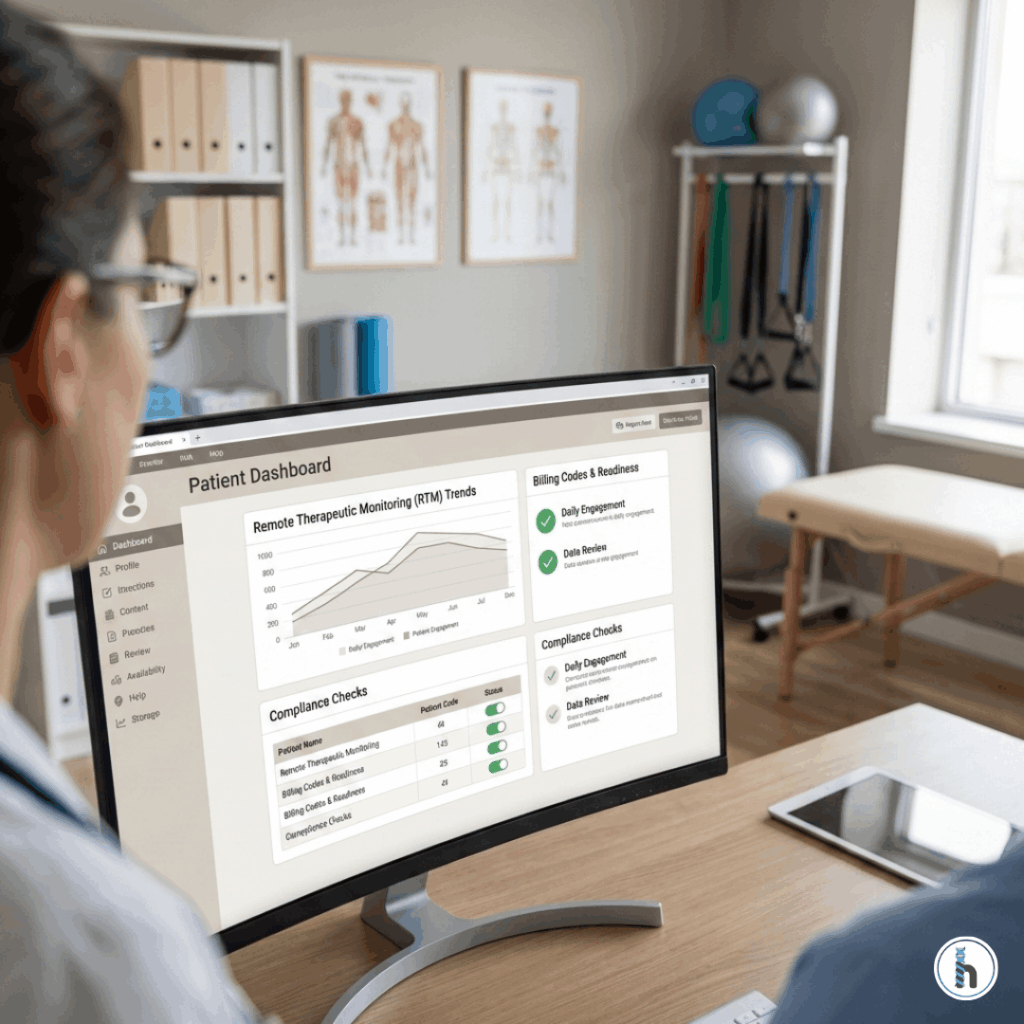
The intricacies of Medicare billing – tracking codes, applying modifiers, ensuring timely submission, managing documentation, and adhering to electronic standards like 837P – can be overwhelming. This is where a robust Electronic Medical Record (EMR) system becomes invaluable for rehabilitation therapy billing.
An EMR designed specifically for therapy practices, like hellonote, can significantly simplify and streamline your Medicare billing workflow. Here is how:
Efficient 837P Generation
A good EMR automatically compiles the necessary data from patient records, treatment notes, and provider information to generate compliant 837P electronic claim files, ready for submission through a clearinghouse or directly to payers. This **837P generation** capability saves immense time.
Reduced Coding and Billing Errors
Many EMRs incorporate features like coding assistance, modifier suggestions based on payer rules, and validation checks that flag potential errors before claims are submitted. This proactive approach helps to **reduce billing errors EMR** systems provide, improving your first-pass acceptance rate.
Integrated Documentation
Linking billing directly to clinical documentation within the EMR ensures that claims are supported by the necessary records, simplifying audits and compliance checks.
Improved Workflow and Tracking
EMR systems provide tools to track claim status, manage denials, and monitor accounts receivable, offering greater visibility and control over your **revenue cycle management EMR** capabilities.
Staying Current
EMR vendors typically update their systems to reflect changes in billing regulations, coding requirements (like annual CPT updates), and electronic transaction standards, helping your practice stay compliant.
By automating many manual steps and providing built-in checks and balances, an EMR like Hellonote frees up valuable time for therapists to focus on patient care and helps administrators manage the financial health of the clinic more effectively.
Take Control of Your Medicare Billing
Understanding the difference between the 837P electronic format and the CMS-1500 form paper form, knowing when each is appropriate, and mastering the key components of accurate claim submission are essential skills for every therapy professional involved in billing. While the rules can seem complex, focusing on accuracy, timely filing, proper coding, supporting documentation, and leveraging technology can transform Medicare billing from a source of frustration into a manageable and efficient process.
Investing in knowledge and the right tools not only ensures compliance but also strengthens the financial foundation of your practice, allowing you to continue providing vital rehabilitation therapy services to your community.
Ready to simplify your Medicare billing for therapy professionals? Explore how Hellonote EMR can help your therapy practice streamline claim submissions, reduce billing errors, and improve revenue cycle management.
Book a Demo now!